The Role of the Federal Reserve in USA Stock Market Performance is one of the most important entities influencing market performance. The Federal Reserve, the country’s central bank, has an important impact on interest rates, investor sentiment, and economic conditions, all of which have an immediate effect on how well the US stock market performs. This article will examine the Federal Reserve in USA Stock Market and how its actions can influence and restrain market movements.

What is the Federal Reserve?
The United States’ central banking system, the Federal Reserve, is in charge of monetary policy supervision and regulation. It was founded in 1913 with the goal of creating a more secure financial system. The Fed’s main goals are to maintain prices, support maximum employment, and moderate long-term interest rates. The Federal Reserve seeks to affect economic activity and maintain financial stability through a variety of instruments and processes, including interest rate setting and open market activities.
The Federal Reserve in USA Stock Market Performance
The Federal Reserve in USA Stock Market have a complicated but indisputable link. A number of crucial elements of the Fed’s policies have the potential to have a big effect on the market:
1. Interest Rate Changes
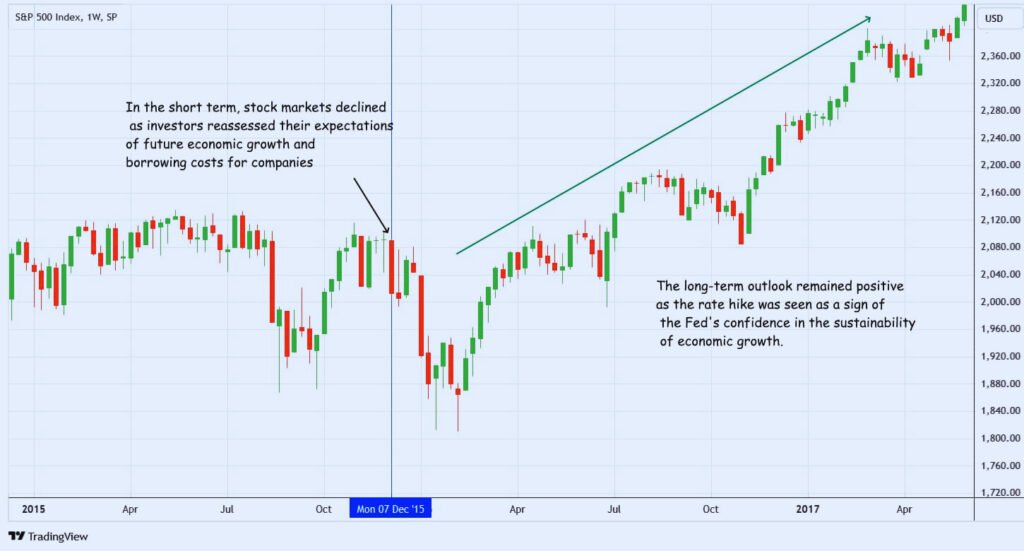
Interest rate changes are one of the Federal Reserve’s most effective instruments for affecting the US stock market. Businesses and individuals pay more to borrow money when the Fed raises interest rates. Usually, this leads to fewer consumer spending and business profits, which can have a negative impact on stock values. On the other hand, when the Fed reduces interest rates, borrowing becomes more affordable, which may increase consumer spending and company investment, both of which can raise stock values.
For example, the Fed may cut interest rates to promote investment and growth in uncertain economic times like recessions. In general, lower rates make equities attractive than bonds, which may lead to better performance in the stock market. So The Role of the Federal Reserve in USA Stock Market Performance is important.

2. Quantitative Easing (QE)
When interest rates are already close to zero, the Federal Reserve employs a non-traditional monetary policy tool called quantitative easing to boost the economy. The Fed purchases long-term assets from the market, such as mortgage-backed securities or U.S. Treasury bonds, as part of quantitative easing. Long-term interest rates are lowered as a result of the financial system’s increased money supply and liquidity. The Fed wants to promote borrowing and investment by doing this.
Because QE increases liquidity, which makes it easier for businesses to borrow at favourable rates and for investors to access capital, the U.S. stock market frequently reacts positively to the boost. As seen by the Fed’s several rounds of quantitative easing during the 2008 financial crisis, this can result in higher stock values.
3. Forward Guidance
The Fed’s communication about its future monetary policy plans, particularly with regard to interest rate decisions, is referred to as forward guidance. The Fed can affect stock market behaviour and set market expectations by indicating that it plans to maintain low interest rates for a long time or to raise them in the future.
For example, investors who expect sustained economic support may interpret the Fed’s announcement that it will maintain low interest rates for the time being as a signal to buy more risky investments like equities. However, stock values may decline if the Fed proposes tight monetary policy as investors prepare for higher borrowing costs and slower economic growth.
4. Inflation Control
Because rising prices have the potential to destabilise the economy and reduce the value of goods, the Federal Reserve also places a high priority on inflation. The Fed frequently changes interest rates to control inflation. The Fed may increase rates to cool the economy and avoid overheated if inflation is too high. Conversely, the Fed may cut rates to boost economic activity if inflation is too low.
The performance of the stock market is frequently impacted by inflation forecasts since investors look for assets that can withstand inflation. Stock prices can change when the Fed expresses concerns about increasing inflation since higher rates have the potential to reduce consumer spending and business earnings
5. Market Sentiment and Confidence
Investor confidence and emotion are greatly influenced by the Federal Reserve. Investor confidence in the economy and stock market is higher when the Fed’s activities are regarded as stabilising, as they are during periods of market volatility or economic uncertainty. On the other hand, market panic or volatility may result from the Fed’s sudden policy adjustments or from its apparent uncertainty.
For example, the Fed helped to stabilise financial markets during the COVID-19 epidemic by acting quickly to lower interest rates and start emergency lending initiatives. The Fed’s prompt and decisive actions boosted the stock market’s rebound and helped rebuild investor confidence.
The Fed’s Influence on Different Market Sectors
Not every area of the stock market is equally impacted by the Federal Reserve’s policies. When interest rates or monetary policy change, some industries typically react more strongly. For example:
- Technology Stocks:Tech stocks typically profit from low interest rates because these businesses frequently depend on borrowing to grow and expand. Investors may find IT companies’ future revenues attractive if rates are reduced.
- Financial Stocks:Banks and other financial institutions can profit from rising interest rates by raising the rates they charge on loans. On the other hand, declining rates may cause their profit margins to contract.
- Consumer Discretionary Stocks: These companies are at risk from shifts in interest rates and consumer confidence since they reflect the items and services that consumers purchase with their own money. Consumer equities may rise as a result of lower interest rates boosting expenditure.
For more updates on our Website.
Conclusion: Federal Reserve in USA Stock Market
The performance of the US stock market is significantly affected by the Federal Reserve. The Fed can affect market movements and investor behaviour by managing inflation, controlling interest rates, and using monetary policy tools including forward guidance and quantitative easing. Investors trying to understand the complex dynamics of the stock market have to understand the Fed’s operations and the economic signals it delivers. Although the Federal Reserve cannot ensure stock market success, its actions have a major impact on the economy and can present investors in the US stock market with both chances and difficulties.
How does the Fed influence the stock market?
By modifying interest rates, managing inflation, conducting fiscal easing, and managing investor expectations through forward guidance, the Fed influences the market.
What happens when the Fed raises interest rates?
Higher borrowing costs due to higher rates can result in lower stock prices and business earnings.
How does inflation control affect stocks?
When inflation is too low, the Fed lowers rates to promote growth; when it is too high, it rises rates to control it, which can hurt stock performance.
Why does market sentiment depend on the Fed?
Market behaviour and investor confidence are impacted by the Fed’s activities, which indicate economic stability or uncertainty.
Which sectors are most affected by the Fed?
Tech Stocks: Benefit from low rates.
Financial Stocks: Profit from higher rates.
Consumer Discretionary: Sensitive to rate changes and consumer confidence.
